Significant Beneficial Ownership - A Step in the Right Direction?
Published: Jun 07, 2021

By Shankar Iyer, Direct Tax Leader, DAA Consulting
BENEFICIAL ownership implies ownership that ultimately enjoys the income from the asset and also controls the asset itself. In 2019, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs ('MCA') - the Indian corporate law authority - notified the rules ('Rules') for determining significant beneficial ownership/owner ('SBO') in Indian companies. Though the concept of beneficial ownership has existed in Indian corporate law for decades, it was essentially based on suo moto disclosure by registered shareholder that the beneficial interest in those shares was in fact held by someone else, i.e., other than the registered shareholder. Rules take this concept further and cast a requirement on companies to identify the SBO.
Rules prescribe that SBO in relation to a reporting company (RCo ), means an individual who (either on his own or together with other person(s)) possesses indirectly or together with direct holdings , at least ten per cent of shares, voting rights thereof, right to receive at least ten per cent of distributable dividend or right to exercise significant influence or control. Indirect holding of right or entitlement is crucial for determining SBO and without any indirect holding there is no SBO.
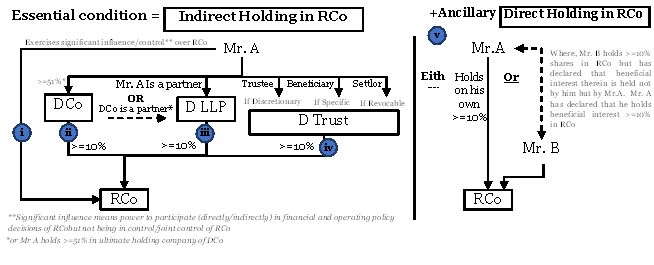
Indirect holding in RCo is contemplated in more ways than one mentioned in (i) to (iv). Direct holding in RCo, contemplated in (v), is optional and only in addition to such indirect holding.
Every individual who acquires SBO in RCo is required to disclose the same in prescribed form and manner to RCo. Once RCo receives such declaration from such individual, it is required to file a return in prescribed form and manner with the Registrar of Companies.
The Rules now cast an obligation on the company to take necessary steps to find out who is the SBO. This becomes relevant when certain individuals (including shareholders) may be acting in concert or in a layered structure with multiple corporate shareholdings in the group shareholding structure. In cases involving a member (not being an individual) holding at least ten per cent shares or voting rights or right to receive dividend thereof, the company (RCo) shall issue notice to such member seeking details of the SBO.
Amongst other things, Rules do not apply to (a) body corporate controlled by Government and (b) SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) registered investment vehicles such as alternative investment funds, mutual funds, real estate investment trusts and infrastructure investment trusts.
Key issues
The Rules have moved the concept of beneficial ownership from being merely based on disclosure by concerned individual shareholder to ensuring the company takes necessary steps to identify SBO. However, in cases where individuals (including the shareholder member) are acting in concert without knowledge of the company i.e., they may not have made any specific disclosure of beneficial ownership/SBO, identifying SBO may be difficult. In such a specific situation, Rules do not prescribe any steps and it is yet to be seen what measures would the company take in order to identify SBO. Further ahead, in case the individuals are relatives, whether their shares would need to be clubbed to test for SBO is unclear. The exercise of significant influence (represented in (i) of above picture) becomes relevant here to determine SBO. What would constitute participation in financial and operating policy decisions of the company is not defined in Rules.
Certain shareholder categories such as private equity investors (not registered with SEBI nor regulated by RBI) often appoint their respective nominees on the board of directors of target companies acquired by them. They also have affirmative voting rights on matters of importance as defined in shareholders' agreement. How and to what extent would Rules for SBO apply to private equity structures is unclear.
Similarly, in a layered structure, the immediate member of the reporting company, holding at least ten percent thereof, is also a corporate entity which in turn is majorly held by another corporate entity and finally an individual holds majority in ultimate holding company in the chain. In this situation, such individual may need to be disclosed as SBO by the company although the effective proportionate share of such individual in reporting company may be well below the stated threshold of ten per cent.
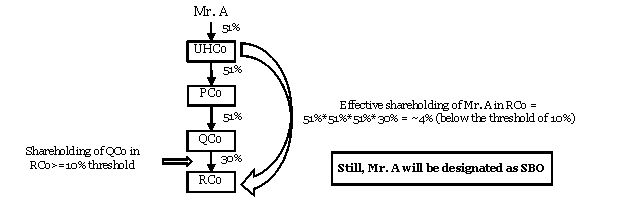
Way forward
The Rules for determining SBO are certainly a step in the right direction to identify real owners of a company. While beneficial ownership was based on disclosure by shareholders, SBO is a step further and requires company to identify its SBO, especially in a layered structure. In case the company fails to take prescribed steps to identify SBO, it shall be punishable with a fine ranging from approx. USD 14,000 to approx. USD 70,000 and additional penalty for continuing offence. The challenges highlighted above, if clarified, would result in seamless implementation of the SBO governance norms and also ensure that the overburdened company courts are spared of frivolous litigation.




